前回の続きです。
組み込みインメモリDBを使う設定
組み込みインメモリDBを使う設定についてです。「src/main/resources/application.yml」に以下の設定を行います。
spring:
datasource:
driverClassName: org.h2.Driver
url: jdbc:h2:mem:testdb;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE
username: sa
password:組み込みインメモリDBの場合、アプリケーションを終了したタイミングでDBデータも削除されます。データを永続化するにはH2データベースを利用する設定が必要です。
H2データベースの利用設定
H2データベースの場合は、先ほどと同じ「src/main/resources/application.yml」に以下の設定を行います。
spring:
datasource:
driverClassName: org.h2.Driver
url: jdbc:h2:file:/tmp/testdb
username: sa
password:これでApp.javaを実行したタイミングでtestdb.h2.dbというファイルが作成されます。こうしておくとアプリケーションを終了してもデータが残るようになります。
補足
上記の永続化対応を行った場合、Schema.splからCREATE tableを実行したとき、すでにテーブルが作成済みだとエラーが発生します。次のように『IF NOT EXISTS』を追加すると回避できます。
Shema.sql
CREATE table IF NOT EXISTS customers(id int primary key auto_increment, first_name varchar(30), last_name varchar(30));
Log4JDBCでSQLログの出力
SQLログを出力する方法についてです。
pom.xmlの設定追加
<dependency> <groupId>org.lazyluke</groupId> <artifactId>log4jdbc-remix</artifactId> <version>0.2.7</version> </dependency>
logback.xmlの準備
「src/main/resources/logback.xml」に以下の設定を書き込む。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<include resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/base.xml"/>
<logger name="jdbc" level="OFF"/>
<logger name="jdbc.sqltiming" level="DEBUG"/>
</configuration>Log4JDBC用のDataSourceの定義
AppConfigクラスを作成
package com.example;
import net.sf.log4jdbc.Log4jdbcProxyDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Autowired
DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties;
DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
DataSource realDataSource() {
DataSourceBuilder factory = DataSourceBuilder
.create(this.dataSourceProperties.getClassLoader()).url(this.dataSourceProperties.getUrl()).username(this.dataSourceProperties.getUsername()).password(this.dataSourceProperties.getPassword());
this.dataSource = factory.build();
return this.dataSource;
}
@Bean
DataSource dataSource() {
return new Log4jdbcProxyDataSource(this.dataSource);
}
}このAppConfigを読み込みためにApp.javaに@ComponentScanを付けます。
package com.example;
import com.example.domain.Customer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public class App implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void run(String... strings) throws Exception {
String sql = "SELECT id, first_name, last_name FROM customers WHERE id = :id";
SqlParameterSource param = new MapSqlParameterSource()
.addValue("id", 1);
Customer result = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, param,
(rs, rowNum) -> new Customer(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("first_name"), rs.getString("last_name")) // (1)
);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
これで準備完了です。アプリケーションを実行時にターミナルにログが出力されるようになります。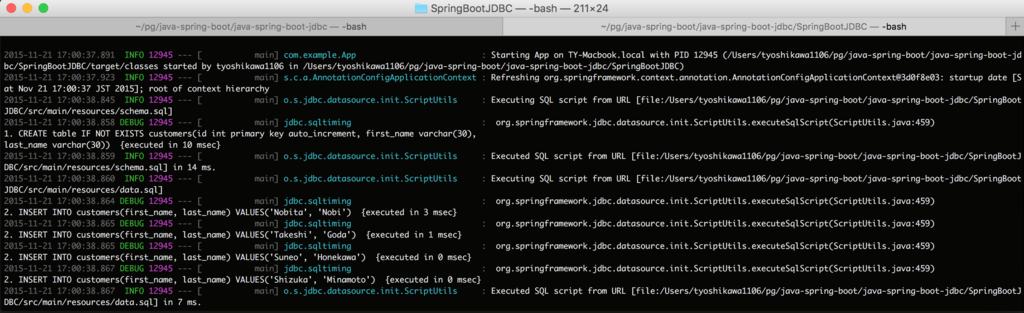
※今回使用したlog4jdbc-remixは開発が終了していてこれからはlog4jdbc-log412を使用した方がいいみたいです。